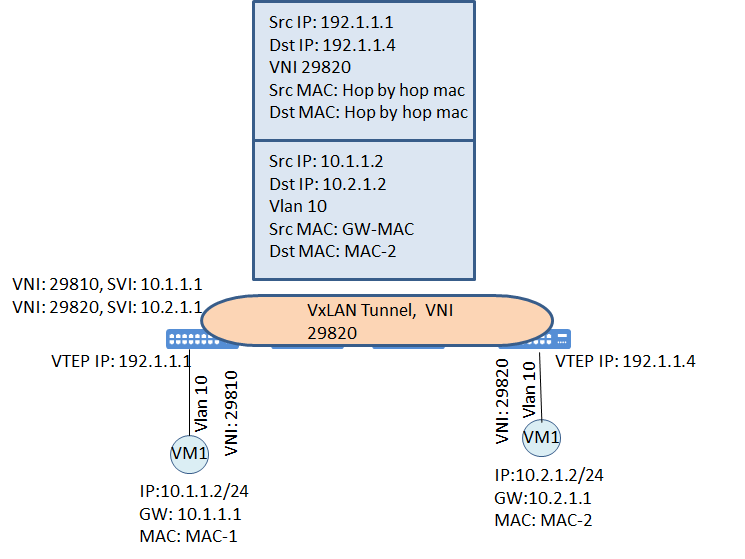
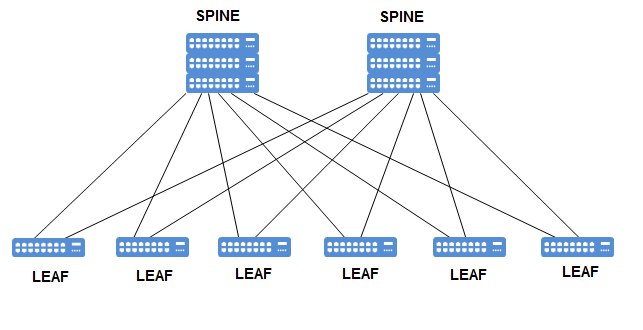
VXLAN allows us to create a logical topologies in the Data Center for our virtual machines. With VxLAN we are able to create a layer 2 network on top of layer 3 infrastructure. In the Data Centers VMs needs to be deployed in a specific segment of the network. These VMs can be moved from …